America’s misunderstood border crisis, in 8 charts
For all the attention on the border, the root causes of migration and the most promising solutions to the US’s broken immigration system are often overlooked.
By Nicole Narea
On May 12, 2024

Herika Martinez/AFP via Getty Images
There is a crisis on America’s border with Mexico.
The number of people arriving there has skyrocketed in the years since the pandemic, when crossings fell drastically. The scenes coming from the border, and from many US cities that have been touched by the migrant crisis, have helped elevate the issue in voters’ minds.
But for all the attention the topic gets, it is also widely misunderstood. The last few decades have seen a series of surges at the border and political wrangling over how to respond. The root causes of migration and why the US has long been ill-equipped to deal with it have been overlooked. Understanding all of that is key to fixing the problem.
Yes, border crossings are up. But the type of migrants coming, where they’re from, and why they’re making the often treacherous journey to the southern border has changed over the years. The US’s immigration system simply was not designed or resourced to deal with the types of people arriving today: people from a growing variety of countries, fleeing crises and seeking asylum, often with their families. And that’s a broader problem that neither Biden, nor any president, can fix on their own.
Here’s an explanation of the border crisis, broken down into eight charts.
It’s true, more people have been coming
The reality at the border has fundamentally changed in the years since Biden took office.
Former President Donald Trump effectively shut down the border during the pandemic. He instituted the so-called Title 42 policy, which expelled asylum seekers under the pretext of protecting public health.
As the pandemic subsided, migrants started attempting anew to cross the border in the last year of Trump’s presidency. When Biden won the 2020 election on a pro-immigrant platform, many migrants reportedly assumed (and were advised by smugglers) that his policies would be more welcoming, resulting in a sharp increase in crossings.
That assumption proved faulty. Biden maintained Trump’s Title 42 policy for more than two years after taking office, ending it only in May 2023 when he also terminated the national emergency related to the pandemic. Border encounters climbed even higher that fall. By December, immigration authorities recorded a record number of more than 300,000 migrant encounters. The number of encounters has been so high that it’s clear more people have been coming under the Biden administration than during the Trump years, even accounting for seasonal fluctuations in migration.
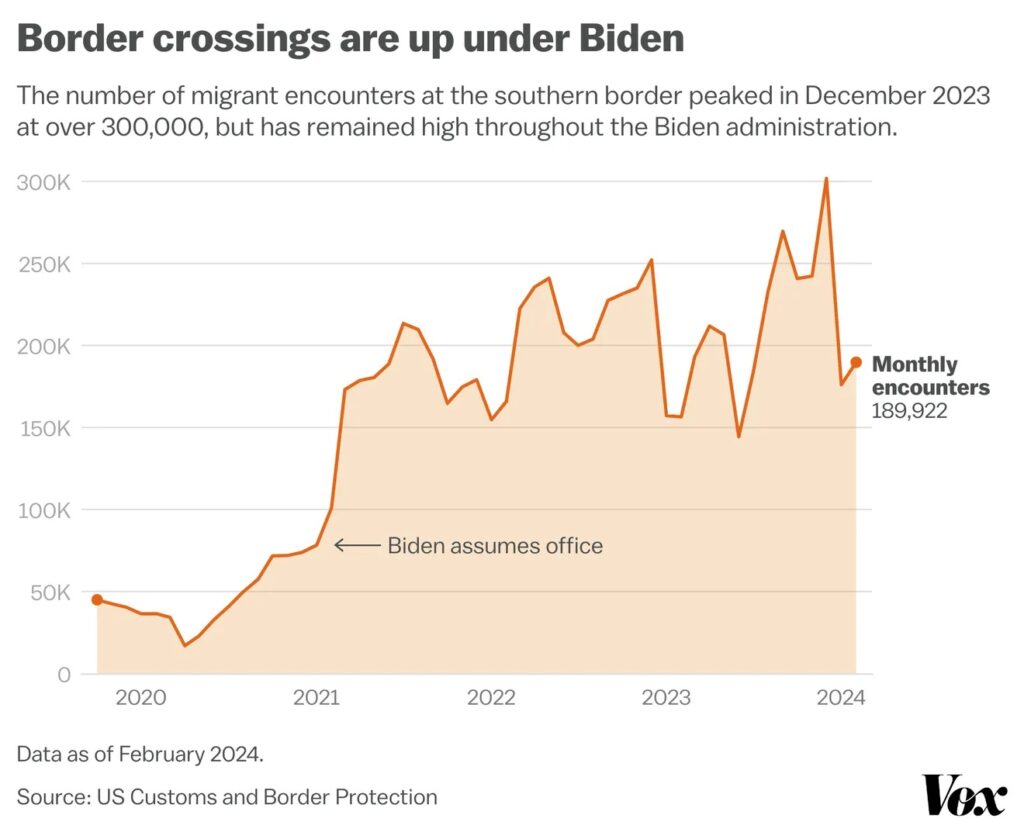
(Note: The same person can account for multiple encounters if they attempt to cross the border and come into contact with officials more than once. While the Title 42 policy was in place, migrants were not penalized for attempting to cross the border multiple times, and many did, though it’s hard to say exactly how many.)
In recent months, however, that trend has started to slow for a few reasons.
The Biden administration has instituted its version of Trump’s asylum transit ban. That rule allows immigration enforcement officials to turn away migrants for a number of reasons: if they do not have valid travel and identification documents, if they’ve traveled through another country without applying for asylum, if they don’t show up at a port of entry at an appointed time, and more.
More so than Biden’s asylum policies, the biggest factor in declining border encounters by far is Mexico’s efforts to step up enforcement, said Aaron Reichlin-Melnick, policy director at the American Immigration Council. Mexico has prevented some migrants from traveling north, bused and flown others back to Mexico’s southern border with Guatemala, and recently reached an agreement with Venezuela to deport its citizens.
That has made this spring so far the quietest at the US southern border in four years. There is a question, however, of how long this can last — and at what cost to asylum seekers.
“Despite Mexico going through the cycle of periodic crackdowns, none of them has lasted for longer than a few months or produced sustained, yearslong drops in the number of migrants arriving at the border,” Reichlin-Melnick said. “That’s why I call it a Band-Aid.”
Compared to past surges, different types of migrants are coming from different places and seeking different things
The last time the US immigration system was significantly reformed in the late 1980s, migrants arriving at the border were primarily single adult males from Mexico looking for work. That is no longer the case.
More people are arriving at the US southern border intending to apply for asylum than ever before. That means instead of coming here claiming to look for work, they are seeking refuge because they have what the US government determines is a “credible fear” of persecution in their home countries on account of their race, religion, nationality, political opinions, or membership in a “particular social group,” such as a tribe or ethnic group.
The number of asylum applications filed as part of immigration court proceedings — where migrants encountered at the border are often referred after being found to have credible claims for protection — skyrocketed in recent years through the end of 2023.
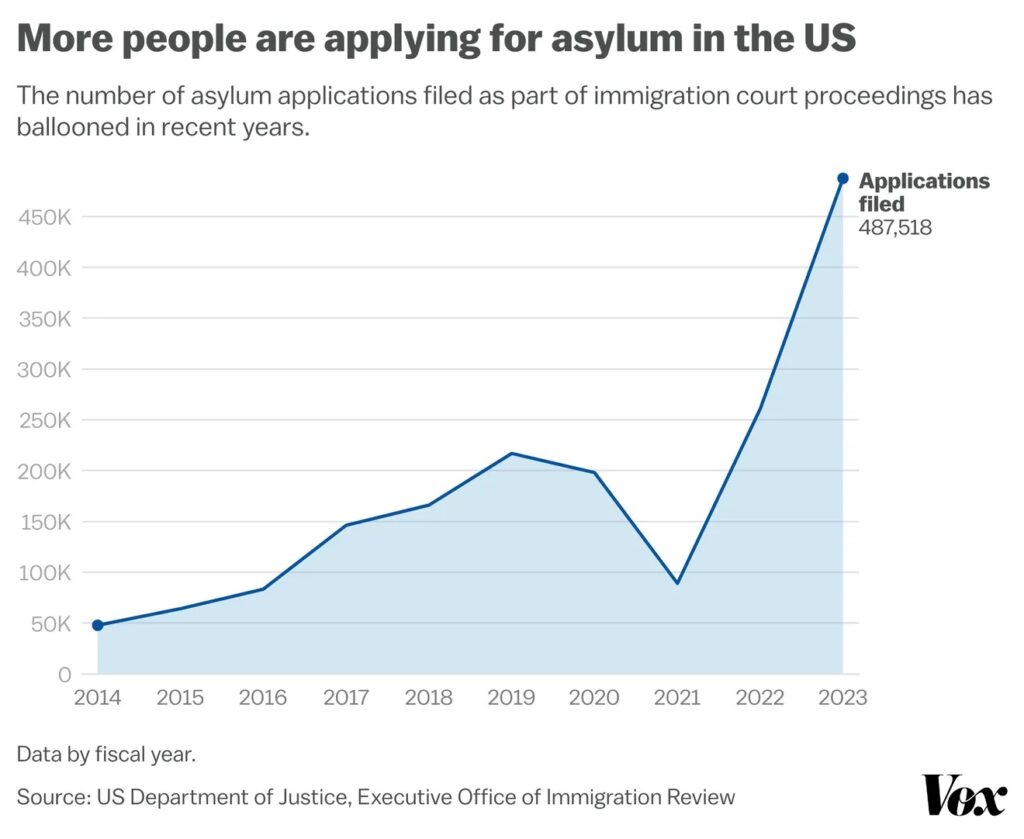
Under the Trump administration, most migrants arriving at the southern border were from Central America’s “Northern Triangle”: Guatemala, Honduras, and El Salvador.
In the last few years, however, the number of migrants coming from those countries has been eclipsed by those coming from South America — particularly Venezuela, Colombia, and Nicaragua — and the Caribbean, including Haiti and Cuba. They have been driven out by recent compounding political and economic crises and natural disasters in their home countries.
Mexican nationals are still showing up at the border, but rather than coming for economic reasons, they’re being driven out by shifting patterns of cartel violence.
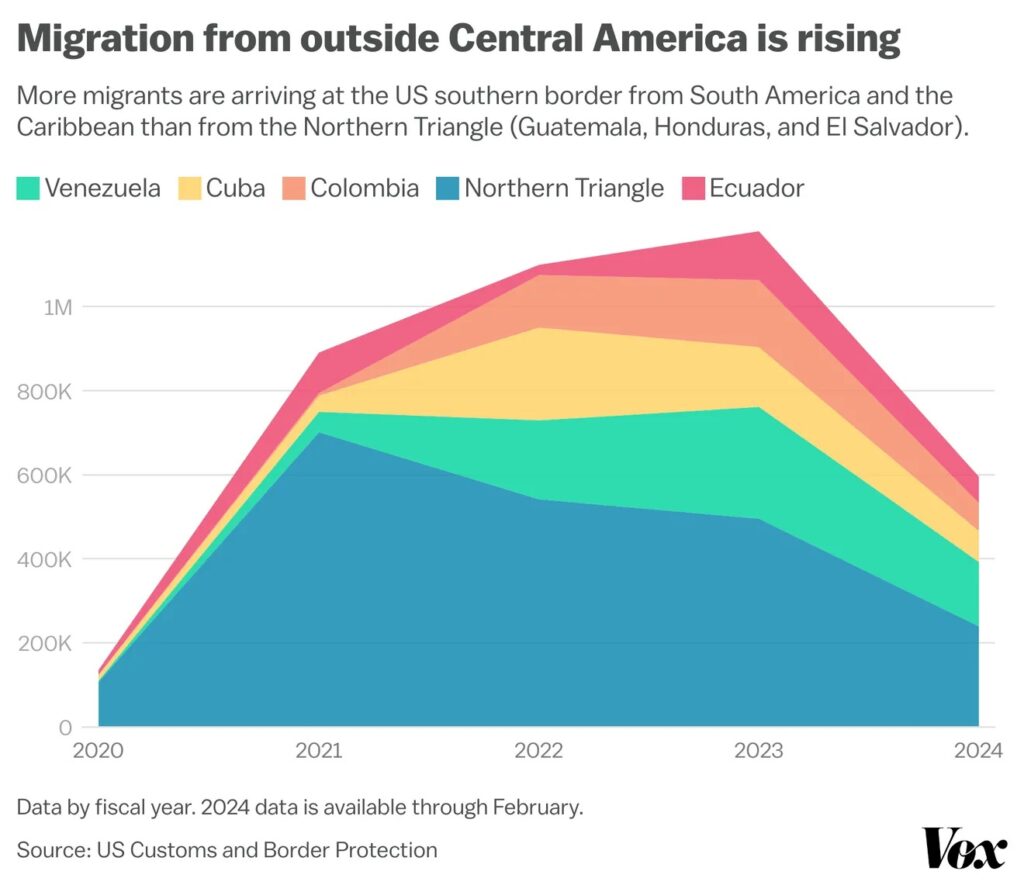
Migrants are increasingly coming from much more far-flung areas of the world. Migrants from China are among the fastest-growing populations at the southern border. There is also rising migration from India and Europe. Smugglers at the southern border have started marketing their services to these populations in a bid to expand their business.
More families are also coming. This might be due to the correct perception that families have a better chance of remaining in the US if they travel together than if they travel separately.
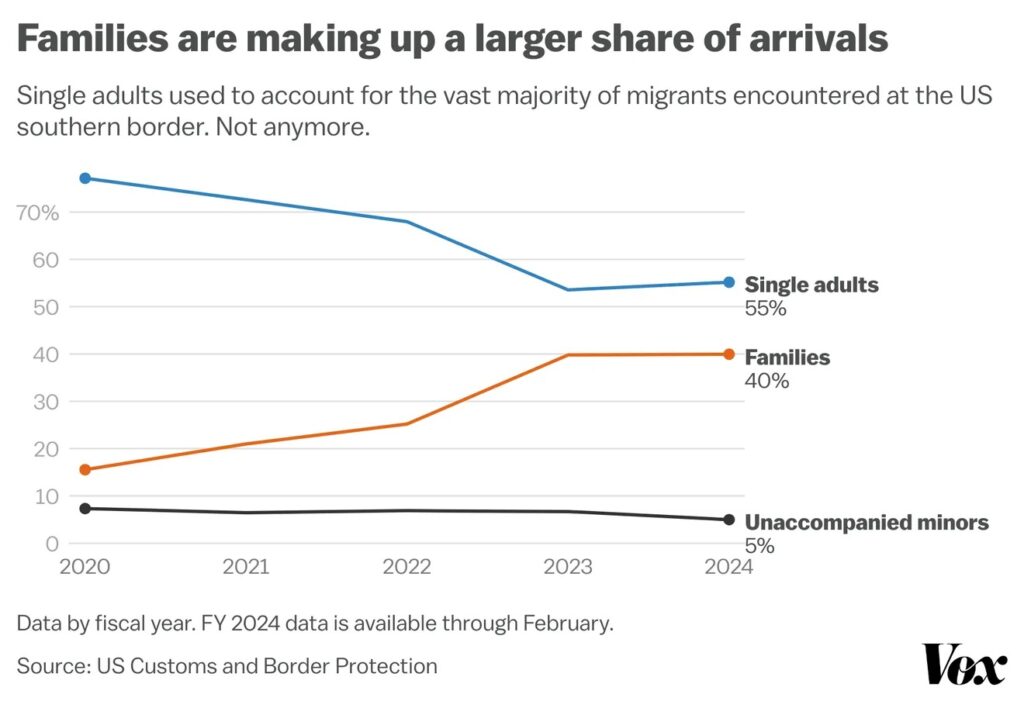
All of this seems to reflect the understanding that, for many of these migrant populations, there are no other good options but to go to the southern border, even if they may qualify to enter the US legally by other means. US refugee resettlement typically takes years. Wait times for some family-based green cards for some countries can take decades.
“There’s an increasing number of people that need protection, and they view that the fastest and clearest way to protection is to go to the US-Mexico border,” said Ariel Ruiz Soto, a senior policy analyst at the Migration Policy Institute.
The immigration system is struggling to absorb these migrants
The US immigration system is not designed to process so many people arriving at the southern border, especially not from such a broad array of countries and as part of families.
That has created a variety of new challenges:
- Some countries generating large numbers of migrants, like Venezuela, Cuba, and China, have refused to receive more than a few, if any, of their citizens whom the US wants to deport.
- Processing migrants who don’t speak Spanish or English may require bringing in a certified translator who isn’t always readily available.
- Families and children are vulnerable populations with a unique set of needs, and the infrastructure does not exist to keep them in government custody long-term. The Biden administration has recently introduced a pilot program to process and monitor families without having to detain them, but like the rest of the immigration system, it is under-resourced and therefore has only covered a fraction of families arriving at the southern border.
These challenges have deepened the immigration court backlog, which has grown to over 3 million cases. The immigration courts handle cases in which the Department of Homeland Security does not have the authority to deport an immigrant unilaterally, and they consider any potential relief from deportation for which they may qualify, including asylum and protections for victims of torture.
So far this year, resolving those cases has taken more than a year on average, during which time migrants may have been detained or released into the US.