TechScape: As the US election campaign heats up, so could the market for misinformation
Twitter is not the only platform inviting political adverts back, as tech giants from Meta to YouTube compete for marketing money and eyeballs
By Kari Paul
On September 5, 2023
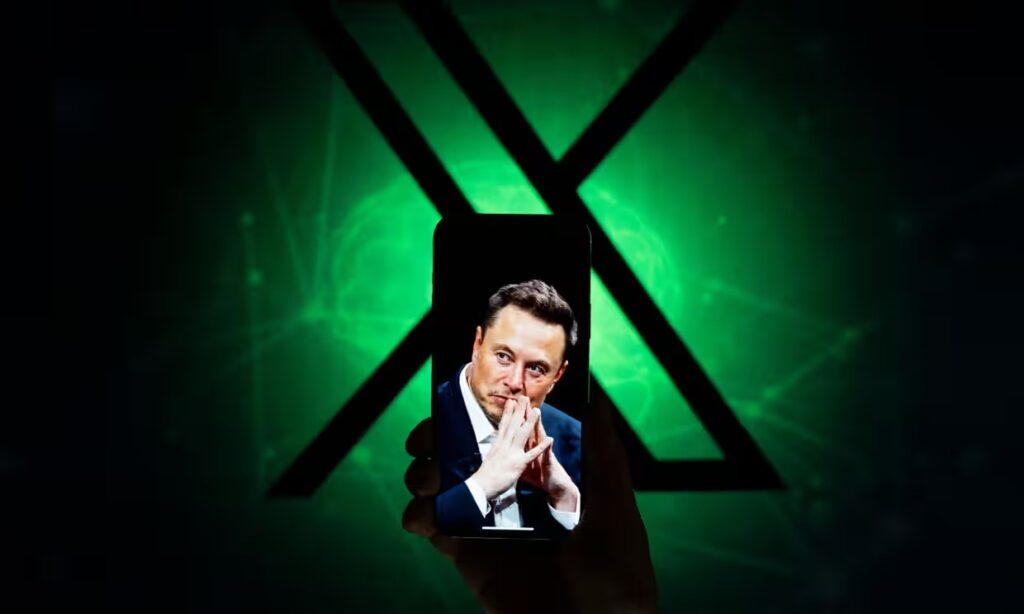

X, the platform formerly known as Twitter, announced it will allow political advertising back on the platform – reversing a global ban on political ads since 2019. The move is the latest to stoke concerns about the ability of big tech to police online misinformation ahead of the 2024 elections – and X is not the only platform being scrutinised.
Social media firms’ handlings of misinformation and divisive speech reached a breaking point in the 2020 US presidential elections when Donald Trump used online platforms to rile up his base, culminating in the storming of the Capitol building on 6 January 2021. But in the time since, companies have not strengthened their policies to prevent such crises, instead slowly stripping protections away. This erosion of safeguards, coupled with the rise of artificial intelligence, could create a perfect storm for 2024, experts warn.
As the election cycle heats up, Twitter’s move this week is not the first to raise major concerns about the online landscape for 2024 – and it won’t be the last.
Musk’s free speech fantasy
Twitter’s change to election advertising policies is hardly surprising to those following the platform’s evolution under the leadership of Elon Musk, who purchased the company in 2022. In the months since his takeover, the erratic billionaire has made a number of unilateral changes to the site – not least of all the rebrand of Twitter to X.
Many of these changes have centered on Musk’s goal to make Twitter profitable at all costs. The platform, he complained, was losing $4m per day at the time of his takeover, and he stated in July that its cash flow was still in the negative. More than half of the platform’s top advertisers have fled since the takeover – roughly 70% of the platforms leading advertisers were not spending there as of last December. For his part, this week Musk threatened to sue the Anti-Defamation League, saying, “based on what we’ve heard from advertisers, ADL seems to be responsible for most of our revenue loss”. Whatever the reason, his decision to re-allow political advertisers could help boost revenue at a time when X sorely needs it.
But it’s not just about money. Musk has identified himself as a “free speech absolutist” and seems hell bent on turning the platform into a social media free-for-all. Shortly after taking the helm of Twitter, he lifted bans on the accounts of Trump and other rightwing super-spreaders of misinformation. Ahead of the elections, he has expressed a goal of turning Twitter into “digital town square” where voters and candidates can discuss politics and policies – solidified recently by its (disastrous) hosting of Republican governor Ron DeSantis’s campaign announcement.
Misinformation experts and civil rights advocates have said this could spell disaster for future elections. “Elon Musk is using his absolute control over Twitter to exert dangerous influence over the 2024 election,” said Imran Ahmed, head of the Center for Countering Digital Hate, a disinformation and hate speech watchdog that Musk himself has targeted in recent weeks.
In addition to the policy changes, experts warn that the massive workforce reduction Twitter has carried out under Musk could impact the ability to deal with misinformation, as trust and safety teams are now reported to be woefully understaffed.
Let the misinformation wars begin
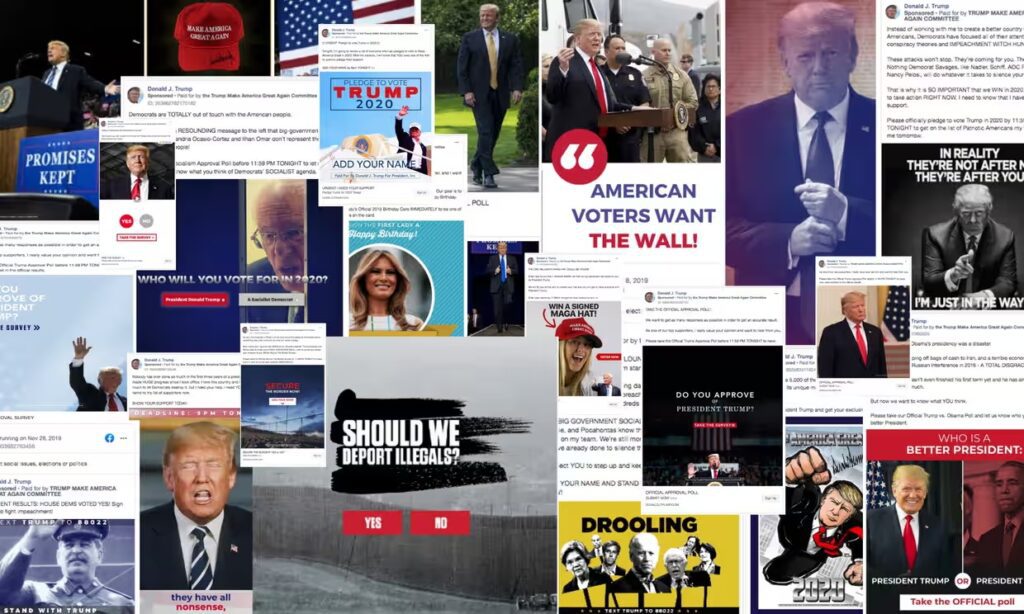
While Musk’s decisions have been the most high profile in recent weeks, it is not the only platform whose policies have raised alarm. In June, YouTube reversed its election integrity policy, now allowing content contesting the validity of the 2020 elections to remain on the platform. Meanwhile, Meta has also reinstated accounts of high-profile spreaders of misinformation, including Donald Trump and Robert F Kennedy Jr.
Experts say these reversals could create an environment similar to that which fundamentally threatened democracy in 2020. But now there is an added risk: the meteoric rise of artificial intelligence tools. Generative AI, which has increased its capabilities in the last year, could streamline the ability to manipulate the public on a massive scale.
Meta has a longstanding policy that exempts political ads from its misinformation policies and has declined to state whether that immunity will extend to manipulated and AI-generated images in the upcoming elections. Civil rights watchdogs have envisioned a worst-case scenario in which voters’ feeds are flooded with deceptively altered and fabricated images of political figures, eroding their ability to trust what they read online and chipping away at the foundations of democracy.
While Twitter is not the only company rolling back its protections against misinformation, its extreme stances are moving the goalposts for the entire industry. The Washington Post reported this week that Meta was considering banning all political advertising on Facebook, but reversed course to better compete with its rival Twitter, which Musk had promised to transform into a haven for free speech. Meta also dissolved its Facebook Journalism Project, tasked with promoting accurate information online, and its “responsible innovation team,” which monitored the company’s products for potential risks, according to the Washington Post.
Twitter may be the most scrutinised in recent weeks, but it’s clear that almost all platforms are moving towards an environment in which they throw up their hands and say they cannot or will not police dangerous misinformation online – and that should concern us all.
This piece was republished from The Guardian.