U.S. Agencies Open Inquiry Into Generic Drug Shortages
The F.T.C. and H.H.S. are examining the tactics of group purchasing organizations that generic industry executives say have led to scarce supplies of treatments like chemotherapy.
By Christina Jewett Feb. 14, 2024
The Federal Trade Commission and the Department of Health and Human Services said on Wednesday that they would examine the causes of generic drug shortages and the practices of “powerful middlemen” that are involved in the supply chain.
The federal agencies’ inquiry is aimed at the group purchasing organizations and drug distributors that have been in the spotlight in recent months as drug shortages reached a 10-year peak. The agencies want to examine the companies’ influence on how the drugs are sold to hospitals and other health facilities, assessing whether the middlemen put pressure on pricing and manufacturing that led to breakdowns.
During Congressional hearings in the last year, oncology experts have testified about the effects of the shortages, describing difficult decisions that forced them to ration key chemotherapy drugs. They detailed month-to-month, sometimes week-to-week, gaps in supplies that were posing deadly risks for some patients.
“For years Americans have faced acute shortages of critical drugs, from chemotherapy to antibiotics, endangering patients,” Lina Khan, the F.T.C. chairwoman, said in a statement. “Our inquiry requests information on the factors driving these shortages and scrutinizes the practices of opaque drug middlemen.”
In earlier interviews with The Times, generic drug industry executives had expressed deepening concerns about their reliance on three major group purchasing organizations for contracts to sell medicines to hospitals and health center customers. The generic executives complained that their companies sometimes offered below-market prices to get big contracts, a strategy that had eroded stability in the industry, especially among makers of sterile injectable products often used in surgical and cancer care.
Drug Shortages in the U.S.
- Federal Agencies’ Inquiry: The Federal Trade Commission and the Department of Health and Human Services said that they would examine the causes of generic drug shortages and the practices of “powerful middlemen” that are involved in the supply chain.
- Chemotherapies: The disruption in supplies of key chemotherapy drugs has realized the worst fears of patients — and of the broader health system — as some people with aggressive cancers have been unable to get the treatment they need.
- Collateral Damage: Parents and doctors are finding that shortages in A.D.H.D. medications are leading to declines in learning and self-esteem among children.
- A Difficult Scarcity: Thousands of Americans have been facing delays in getting drug treatments for life-threatening diseases, forcing patients and their doctors to face grim realities.
Lawmakers have echoed the concerns. Late last year, Senator Ron Wyden, a Democrat of Oregon and chairman of the Senate Finance Committee, criticized “very powerful health care middlemen” in the generic drug industry. Last month, he and Senator Mike Crapo, a Republican of Idaho, outlined ways to limit drug shortages, focusing in part on proposed changes to Medicare payments for sterile injectable drugs.
Dr. Robert Califf, the commissioner of the Food and Drug Administration, testified in Congress last year about the limits to the agency’s ability to manage drug shortages, pointing to market dynamics — such as low and falling prices — in the generic drug industry.

Chemotherapy drug shortages have become headlines for lawmakers and the drug industry. Cancer specialists have been forced to draft treatment guidelines that recommended giving scarce doses to those patients who had a chance at a cure — and denying them to patients with metastatic disease who wanted to live longer.
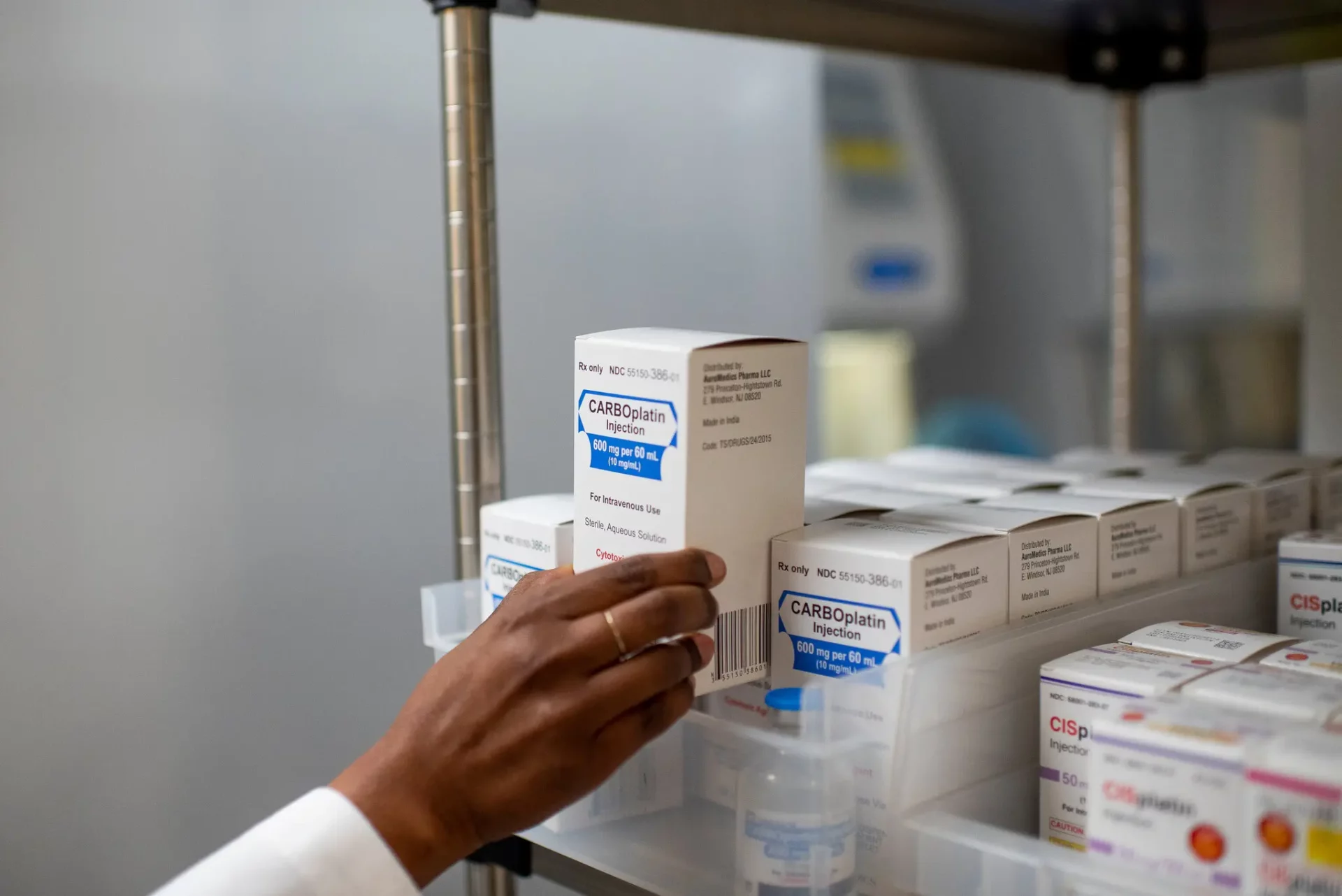
The key chemotherapy drugs that have been in shortage, cisplatin and carboplatin, are crucial for treating lung, breast, testicular, ovarian and head and neck cancers. In recent years, prices of both drugs fell to about $15 to $20 a dose, even as Intas Pharmaceuticals, a drugmaker headquartered in India, gained market share.
Intas paused making the drugs amid quality concerns raised by a surprise F.D.A. inspection late in 2022. That resulted in the wider shortages, which generic drug industry executives pointed to as an example of how falling prices and winner-take-all contracts increased reliance on fewer drug makers.
The F.T.C. inquiry announced Wednesday is focused on whether concentration among the drug industry intermediaries “has disincentivized suppliers from competing in generic drug markets.” The agency is accepting public comments as part of its inquiry into the shortages.
The Association for Accessible Medicines, a trade group for the generic drug industry, commended the F.T.C. for trying to address the issue. David Gaugh, the group’s interim president, said in a statement that it was important for the agency to look at lower generic drug prices, concentration among intermediary companies and the decline in manufacturing sites.
“As a result of all of this, the risk of drug shortages will only increase without action to bolster the long-term sustainability of generic manufacturing,” Mr. Gaugh said in a statement.
The federal inquiry is expected to look into the three main group-purchasing organizations that contract with generic drug makers to supply drugs to hundreds of customers. Todd Ebert, president of the Healthcare Supply Chain Association, which represents group purchasers, said the companies provide competitive prices to hospitals and other health care providers — as well as a reliable drug supply.
“G.P.O.s help stabilize the market for generic drugs by working with manufacturers on contracts that provide the certainty and predictable demand they need to remain in the market,” Mr. Ebert said in a statement. He added that the organization looks “forward to sharing more with the F.T.C. about the critical role of G.P.O.s in addressing the ongoing drug shortage crisis.”
John Parker, a spokesman for the Healthcare Distributors Alliance, which represents major companies such as McKesson, Cardinal Health and AmerisourceBergen that assess fees to generic drug makers to transport their drugs, said the group was aware of the agencies’ request for information and would provide its perspective to them at a later date.
A correction was made on Feb. 15, 2024: An earlier version of this article misstated the view of the Healthcare Distributors Alliance, a group that represents major companies. A spokesman for the alliance did respond to a request for comment from The Times.
Christina Jewett covers the Food and Drug Administration, which means keeping a close eye on drugs, medical devices, food safety and tobacco policy. More about Christina Jewett
This article was originally published by The New York Times.